Compare and contrast the theories of plate tectonics and continental drift with key differences, historical context, real-world applications, and FAQs. Perfect for geology students and academic paper buyers worldwide.
For geology students navigating the complex world of Earth science, two foundational concepts—plate tectonics and continental drift—often appear confusingly similar. However, while both theories seek to explain the movement of Earth’s continents, their scientific roots, supporting evidence, and modern-day relevance differ significantly. Understanding these differences isn’t just critical for exam success—it helps students comprehend natural disasters, resource exploration, and Earth’s ever-changing face.
In this article, we will compare and contrast the theories of plate tectonics and continental drift, highlighting five essential differences, evidence for each theory, real-world applications, and why students around the world often seek help with this topic through platforms like Study Creek and Dissertation Hive.
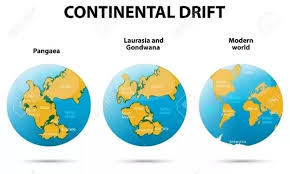
The continental drift theory was proposed by German meteorologist Alfred Wegener in 1912. He suggested that Earth’s continents were once joined together in a single landmass called Pangaea, which later broke apart, causing the continents to drift to their current positions.
Today, Wegener is celebrated as a pioneer whose ideas laid the foundation for modern geology.
The plate tectonics theory emerged in the 1960s as a more comprehensive explanation of Earth’s lithospheric movements. Unlike continental drift, it provided a clear mechanism—convection currents in the mantle—to explain the movement of continents.
The theory of plate tectonics has become the unifying theory in geology, explaining both continental movement and ocean floor dynamics.
Here’s a side-by-side breakdown to compare and contrast the theories of plate tectonics and continental drift:
| Feature | Continental Drift | Plate Tectonics |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed By | Alfred Wegener (1912) | Multiple scientists, refined in 1960s |
| Driving Force | Not explained | Convection currents in the mantle |
| Scope | Only continents | Entire lithosphere, including oceanic crust |
| Evidence | Fossils, rocks, fit of continents | Seafloor spreading, GPS data, paleomagnetism |
| Scientific Acceptance | Initially rejected | Universally accepted in modern geology |
Image Alt Text: Comparison table showing 5 differences between plate tectonics and continental drift theories.
This clear comparison reveals that while both theories aim to explain Earth’s dynamic surface, plate tectonics is broader, stronger, and scientifically complete.
Understanding how and why Earth’s plates move has practical implications for:
Video Suggestion: National Geographic: Plate Tectonics Explained in 5 Minutes
Understanding tectonic theory is not just academic—it’s vital for survival and sustainability.
College and university students across the globe—from the U.S. and UK to India, Nigeria, Kenya, and Australia—frequently search or pay for geology paper help on topics like this one. Here’s why:
Use platforms offering custom geology essays written by experts, ensuring clarity, plagiarism-free content, and high grades.

Q1: What is the main difference between continental drift and plate tectonics?
A: Continental drift describes the movement of continents without explaining the mechanism, while plate tectonics explains movement using convection currents and includes oceanic crust.
Q2: Why was Wegener’s theory initially rejected?
A: He lacked a mechanism to explain how continents moved, which made the theory scientifically incomplete.
Q3: What evidence supports plate tectonics?
A: Seafloor spreading, paleomagnetism, earthquake data, and satellite GPS all confirm plate tectonic movements.
Q4: Can I get a paper written on this topic?
A: Yes! Services like Dissertation Hive and Study Creek offer custom papers tailored for geology students.
Q5: Are tectonic plates still moving today?
A: Yes. Plates move at an average rate of 1–10 cm per year, causing earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain formation.
Q6: How does this topic apply in real life?
A: It helps in urban planning, disaster prediction, and natural resource management.

To truly understand Earth’s behavior, students must move beyond just memorizing facts. Comparing and contrasting the theories of plate tectonics and continental drift reveals the evolution of geological science—from Alfred Wegener’s bold idea to the detailed, evidence-based framework we use today.
While continental drift sparked a revolution in Earth science, it is the plate tectonics theory that provides a comprehensive explanation of how and why Earth’s surface moves.
As global students increasingly seek academic writing support on complex topics like this, it’s crucial to ensure that content is accurate, engaging, and scientifically grounded—just like this article. For those who need more in-depth guidance, reputable platforms like Study Creek and Dissertation Hive are only a click away.
Name:
Institution:
Course: Earth Science 204: Natural Disasters and Geohazards
Instructor:
Date:
Title: The Causes and Effects of Volcanic Eruptions in Different Geological Settings
Volcanic eruptions are among the most dramatic natural phenomena affecting Earth. This paper explores the diverse causes of volcanic activity and the varying consequences of eruptions based on geological settings, such as divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, and hotspots. It highlights real-world examples, evaluates human and environmental impacts, and provides insight into the importance of understanding volcanoes in modern geology and hazard management.
Volcanoes are dynamic features of the Earth’s crust formed by the movement of molten rock or magma from beneath the surface to the exterior. These natural features are shaped by internal geologic processes and vary widely depending on their tectonic context. From the explosive power of Mount St. Helens to the slow lava flows in Hawaii, the causes and effects of volcanic eruptions differ drastically across divergent, convergent, and intraplate settings. This paper investigates the main geological causes and the effects—both immediate and long-term—of volcanic activity in various tectonic environments.
Volcanic eruptions are caused primarily by the movement and melting of tectonic plates that allow magma to rise to the surface. These processes occur in different geological settings:
At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates move apart. As the plates separate, magma rises from the mantle to fill the gap, creating new crust. This setting is common under the ocean, forming mid-ocean ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
At these boundaries, an oceanic plate subducts beneath a continental or another oceanic plate. The subducting plate melts as it sinks into the mantle, leading to the formation of magma.
Hotspots are areas of volcanic activity located away from tectonic boundaries, caused by mantle plumes.
The effects of volcanic eruptions vary by location, eruption style, and magnitude. These can be categorized as:
Volcanic hazards affect millions globally. Key areas of impact include:
Setting: Divergent boundary, Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Impact: Ash cloud grounded European flights for 6 days; massive economic loss (~$1.7 billion).
Significance: Showed global interconnectedness and vulnerability to ash dispersion.
Setting: Convergent boundary, Eurasian and Philippine Sea plates.
Impact: 800+ deaths, 1.2 million displaced, global temperature drop of 0.5°C.
Scientific Breakthrough: Forecasting improved due to collaboration between USGS and PHIVOLCS.
Source: USGS Report on Mt. Pinatubo
Setting: Hotspot
Impact: 700 homes destroyed, dramatic increase in lava tourism, new coastline created.
Lava Type: Fluid basalt, low explosivity but widespread damage.
Volcanic eruptions are complex geologic events with diverse causes and far-reaching effects. Whether occurring along divergent boundaries, subduction zones, or mantle hotspots, the forces that drive volcanoes shape Earth’s surface and profoundly affect life. Understanding these processes helps communities prepare for disasters, capitalize on geothermal resources, and respect the dynamic nature of our planet.
Note: Students can explore custom academic support through platforms like Study Creek and Dissertation Hive for professionally written essays on geology and Earth science topics.
Delivering a high-quality product at a reasonable price is not enough anymore.
That’s why we have developed 5 beneficial guarantees that will make your experience with our service enjoyable, easy, and safe.
You have to be 100% sure of the quality of your product to give a money-back guarantee. This describes us perfectly. Make sure that this guarantee is totally transparent.
Read moreEach paper is composed from scratch, according to your instructions. It is then checked by our plagiarism-detection software. There is no gap where plagiarism could squeeze in.
Read moreThanks to our free revisions, there is no way for you to be unsatisfied. We will work on your paper until you are completely happy with the result.
Read moreYour email is safe, as we store it according to international data protection rules. Your bank details are secure, as we use only reliable payment systems.
Read moreBy sending us your money, you buy the service we provide. Check out our terms and conditions if you prefer business talks to be laid out in official language.
Read more